AI VS Deep Learning VS Machine Learning
AI or Artificial Intelligence is an approach in computer science, which aims to give a computer
system abilities to learn and solve problems without human participation.
Machine Learning is a division of AI, which allows computer system to improve itself on basis of
incoming data. There are many of different algorithms in this part for each specialized on particular
class of tasks.
Deep Learning in it's turn is a part of Machine Learning, which tries to replicate known patterns
of biological brain in the computer system. It's used in various ML algorithms. Usually this technique
represented as multi-layered neuron structure.
Supervised Learning
This method of learning work similar to learning of a child. It realizes under control of some supervisor. Every result of an algorithm is checked and supervisor provides a feedback on it. Using this feedback algorithm tries to improve it's future results.
During training in this approach, providing some test data to algorithm, the result is already known. We just give the input data, get the result, compare it with desired outcome and provide necessary feedback.
Such datasets with known results called labeled. For example we are trying to teach algorithm to
recognize fruits from given pictures. We should have a dataset with different fruit pictures, labeled with
their names. This is labeled dataset.
This method is often used for classification problems.
Examples of supervised learning algorithms:
- Decision Trees,
- K-Nearest Neighbor,
- Linear Regression,
- Support Vector Machine and
- Neural Networks.
Unsupervised Learning
On the other side unsupervised learning happens without third party supervision. The system should learn
by itself from provided dataset and the outcome will not be matched with predefined desired result.
Datasets for this approach are also in contradiction with supervised learning are unlabeled.
Types Of Unsupervised Algorithms
-
Clustering Algorithm: The methods of finding the similarities between data items such as the same shape, size, color, price, etc. and grouping them to form a cluster is cluster analysis. -
Outlier Detection: In this method, the dataset is the search for any kind of dissimilarities and anomalies in the data. For example, a high-value transaction on credit card is detected by the system for fraud detection. -
Association Rule Mining: In this type of mining, it finds out the most frequently occurring item sets or associations between elements. Associations such as “products often purchased together”, etc. -
Autoencoders: The input is compressed into a coded form and is recreated to remove noisy data. This technique is used to improve image, and video quality.
Reinforcement Learning
In this kind of learning algorithms takes into account and feedback and also past experience. It takes into account previous step results. Than more steps performed, than more precise will be next step result.
It is often used in self-driving cars.
Some algorithms:
- Q-Learning,
- Deep Adversarial Networks
- Temporal Difference
Neural Network
Artificial Neural Network is analogous to biological neural network, which is a structure of billions
of interconnected neurons. This network has ability to learn from it's actions on training data.
There are following characteristics for neural network:
Non Linearity: The mechanism followed in ANN for the generation of the input signal is nonlinear.Supervised Learning: The input and output are mapped and the ANN is trained with the training dataset.Unsupervised Learning: The target output is not given, so the ANN will learn on its own by discovering the features in the input patterns.Adaptive Nature: The connection weights in the nodes of ANN are capable to adjust themselves to give the desired output.Biological Neuron Analogy: The ANN has a human brain-inspired structure and functionality.Fault Tolerance: These networks are highly tolerant as the information is distributed in layers and computation occurs in real-time.
Neural network consists of several layers of neurons:
input layer- this is a first layer with input neurons. Amount of input neurons equal to input parameters. There is only one input layer.hidden layers- actual calculation happens inside these hidden layers. There may be one or more hidden layers.output layers- hidden layers connect to this single output layer, which returns output results.
Each node or neuron has activation function which defines, how input value will be modified into output neuron value and weight also called
synapse, which contains information about the input signal.
Neuron receives an inputs, with some weights. Weighted sum of these inputs will be neuron's input value. These value goes through activation function and calculates output value, which will be sent into next neurons.
Weighted sum of inputs is a product of all weighted of all inputs.
There are common architectures of artificial neural networks:
Single-Layer Feed-Forward Network
In this network there are only input and output layers and each neuron of input layer is connected to each neuron of output layer.
feed-forward means that there is no feedback from output layer to input.
Multi-Layer Feed-Forward Network
Same as previous, but with one or more intermediate hidden layers between input and output layers.
Single Node With Its Own Feedback
Contains single node with feedback from output.
Single-Layer Recurrent Network
In a single layer recurrent network, the feedback network forms a closed loop. In this model, a single neuron receives feedback to itself or the other neurons in the network or both.
Multi-Layer Recurrent Network
In Multi-Layer recurrent network, multiple hidden layers exist and the output is redirected back to the neurons of the previous layers and other neurons in the same layers or same neuron itself.
Feed forward neural network consists of two main components - neurons and synapses.
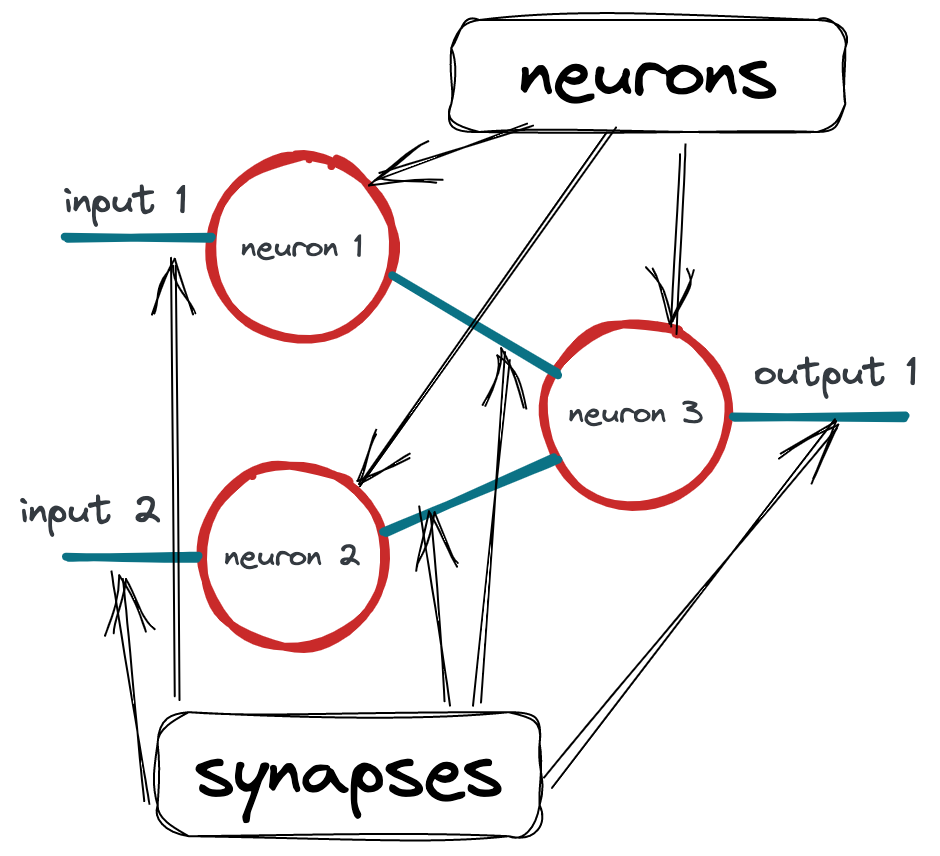
On this example we see simple neural network with 3 neurons and 5 synapses. There are two layers - inputs and outputs layers. There may be more layers with arbitrary number of neurons. These middle layers are called hidden. But on input and output layers we have same amount of neurons as we have input sources and outputs we want to receive.
The more layers and neurons neural network has, the more advanced and abstract concept it can handle.
Basic principle of FFNN - send some numbers to the inputs, than neural network propagating these
values through it's neurons, which change the values somehow. This is called feedforwarding. And
on the output we receive some changed numbers, which in their turn will be an answer.
For the neural network this is only numbers and their respective change. We give these numbers their meaning. For example, we send to the neural network a picture as a bite array and on single output we have a number between 0 and 1. We decide, that this output means presence or absence of some object on the provided image. Initially all outputs of our network may be completely useless. We need to train neural network. Feeding it with some data set and giving a feedback we seek a moment, when it will return proper output. From now on we can consider our neural network trained and can feed it with some new data, which it does not know yet and with high probability will get meaningful results.
neurons are processing unit, which has at least one input and output. It receives some value,
changes it with some criteria and returns changed value into output. Neuron has a bias, which
works similarly to threshold - when input value is big enough it will be propagated, otherwise will
output 0.
synapses are connections between neurons. Each synapse has weight, which is a multiplicator on
a value, transferred through this synapse.
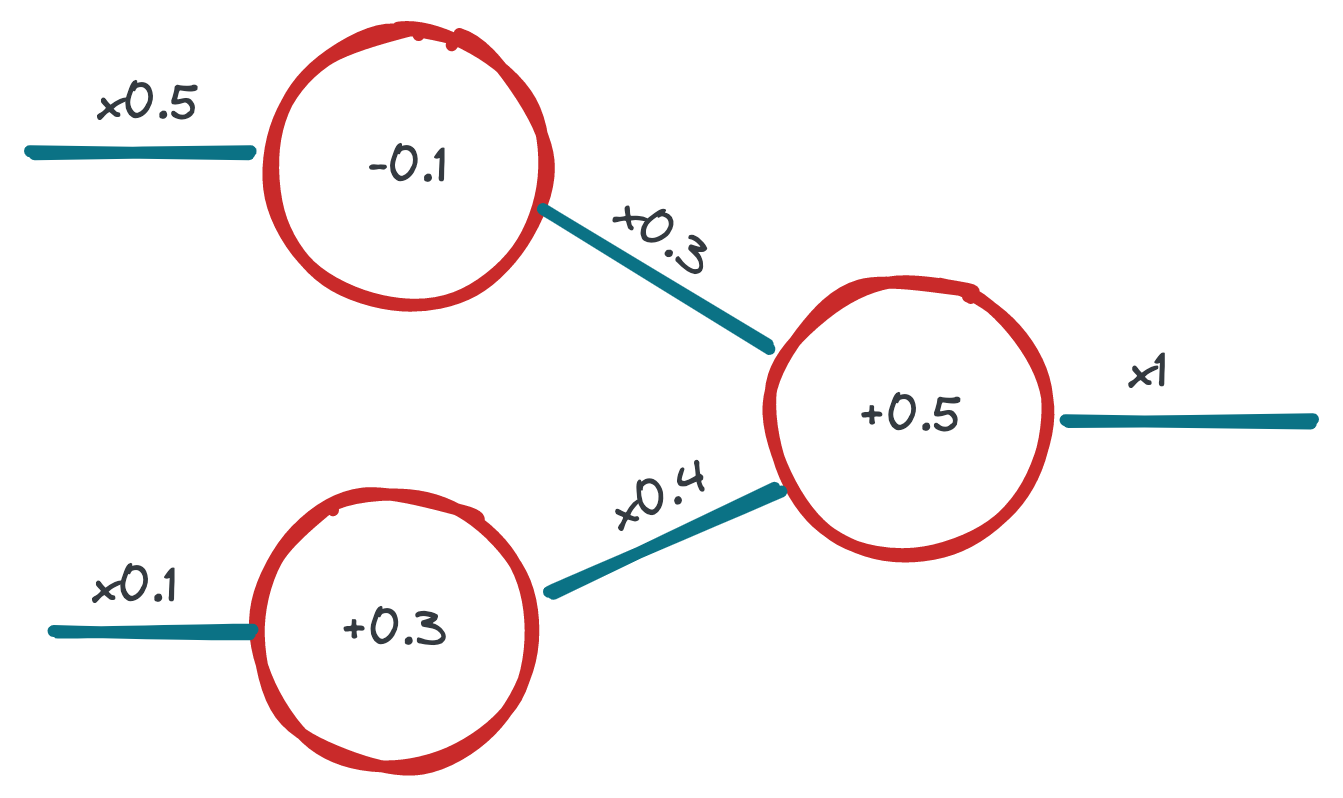
On the first attempt we can give weights and biases totally random values. And then we need to train
neural network in order to get meaningful results. To do that some algorithms used, for example
back propagation. It works like that: network is feed with some amount of different data, it
responds to it and here we need to tell it the correct result it should have been responded with.
Back propagation goes back on neural network, adjusting weights and biases accordingly. This
approximates future results.
Important to note, that this learning may improve results to some close point or stop on local optimum and not improve further.
Back propagation is good, when we have rich set of data with certain output.